Frequency-specific neuromodulation of local and distant
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 14 abril 2025

A growing literature has focused on the brain’s ability to augment processing in local regions by recruiting distant communities of neurons in response to neural decline or insult. In particular, both younger and older adult populations recruit bilateral prefrontal cortex (PFC) as a means of compensating for increasing neural effort to maintain successful cognitive function. However, it remains unclear how local changes in neural activity affect the recruitment of this adaptive mechanism. To address this problem, we combined graph theoretical measures from functional MRI (fMRI) with diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in order to resolve a central hypothesis: how do aged brains flexibly adapt to local changes in cortical activity? Specifically, we applied neuromodulation to increase or decrease local activity in a cortical region supporting successful memory encoding (left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex or DLPFC) using 5Hz or 1Hz rTMS, respectively. We then assessed a region’s local within-module degree (WMD), or the distributed between-module degree (BMD) between distant cortical communities. We predicted that (1) local stimulation-related deficits may be counteracted by boosting BMD between bilateral PFC, and that this effect should be (2) positively correlated with structural connectivity. Both predictions were confirmed; 5Hz rTMS increased local success-related activity and local increases in PFC connectivity, while 1Hz rTMS decreases local activity and triggered a more distributed pattern of bilateral PFC connectivity to compensate for this local inhibitory effect. These results provide an integrated, causal explanation for the network interactions associated with successful memory encoding in older adults.
Biology, Free Full-Text

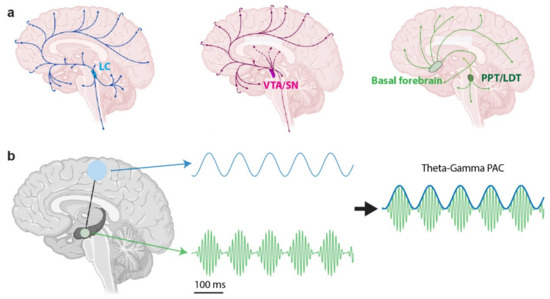
Local extracellular K+ in cortex regulates norepinephrine levels
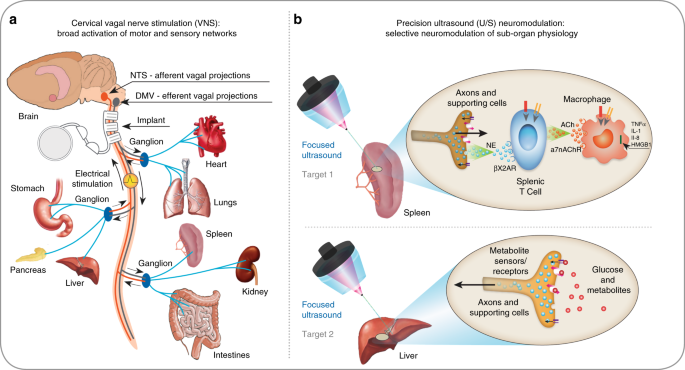
Noninvasive sub-organ ultrasound stimulation for targeted

Focused Ultrasound Neuromodulation and the Confounds of
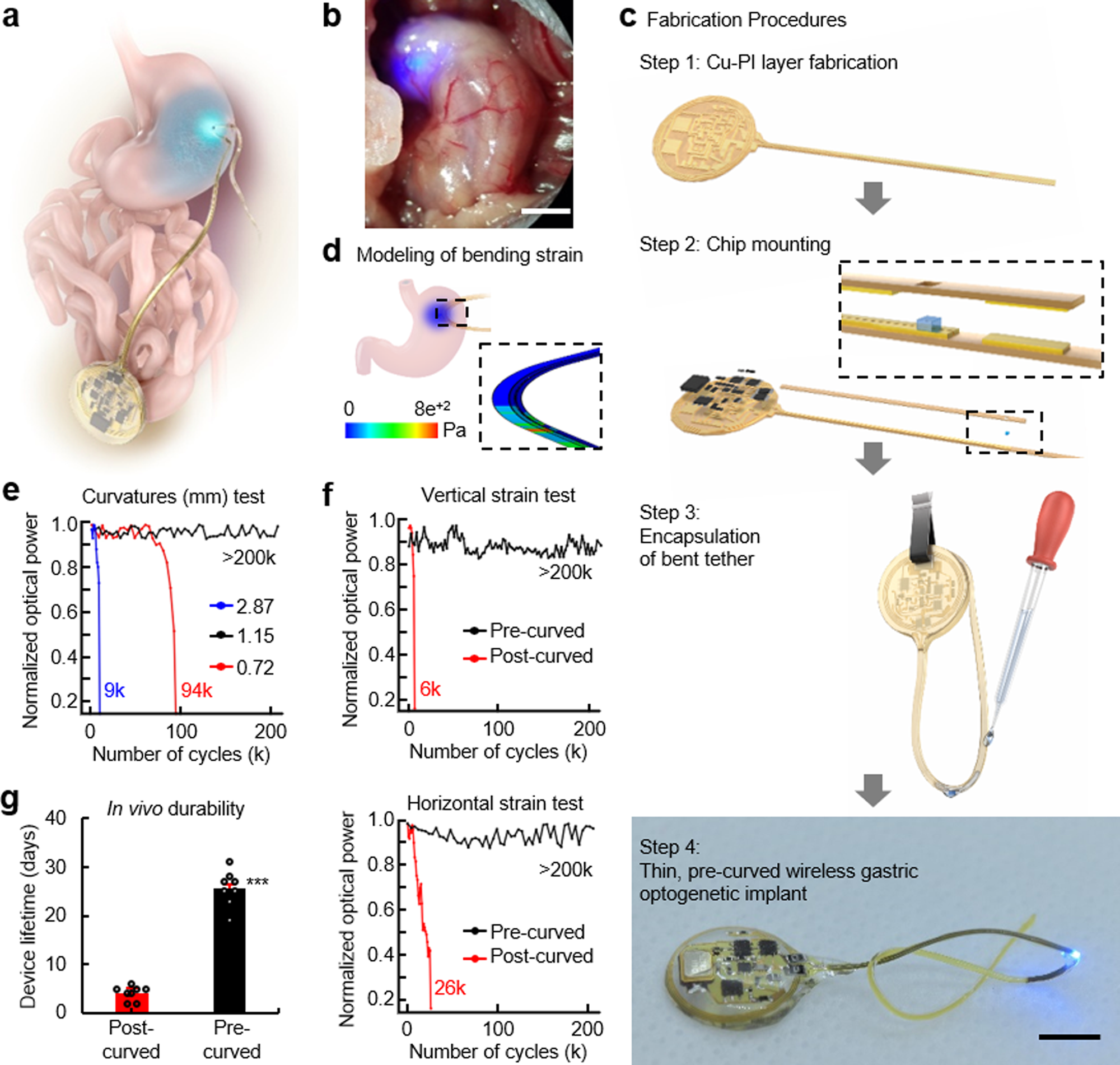
Organ-specific, multimodal, wireless optoelectronics for high

Frequency-Dependent Action of Neuromodulation
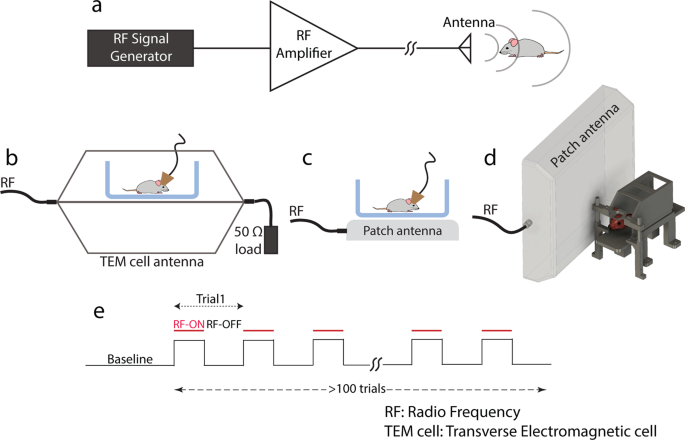
Neuronal activity under transcranial radio-frequency stimulation

Focused Ultrasound Neuromodulation and the Confounds of
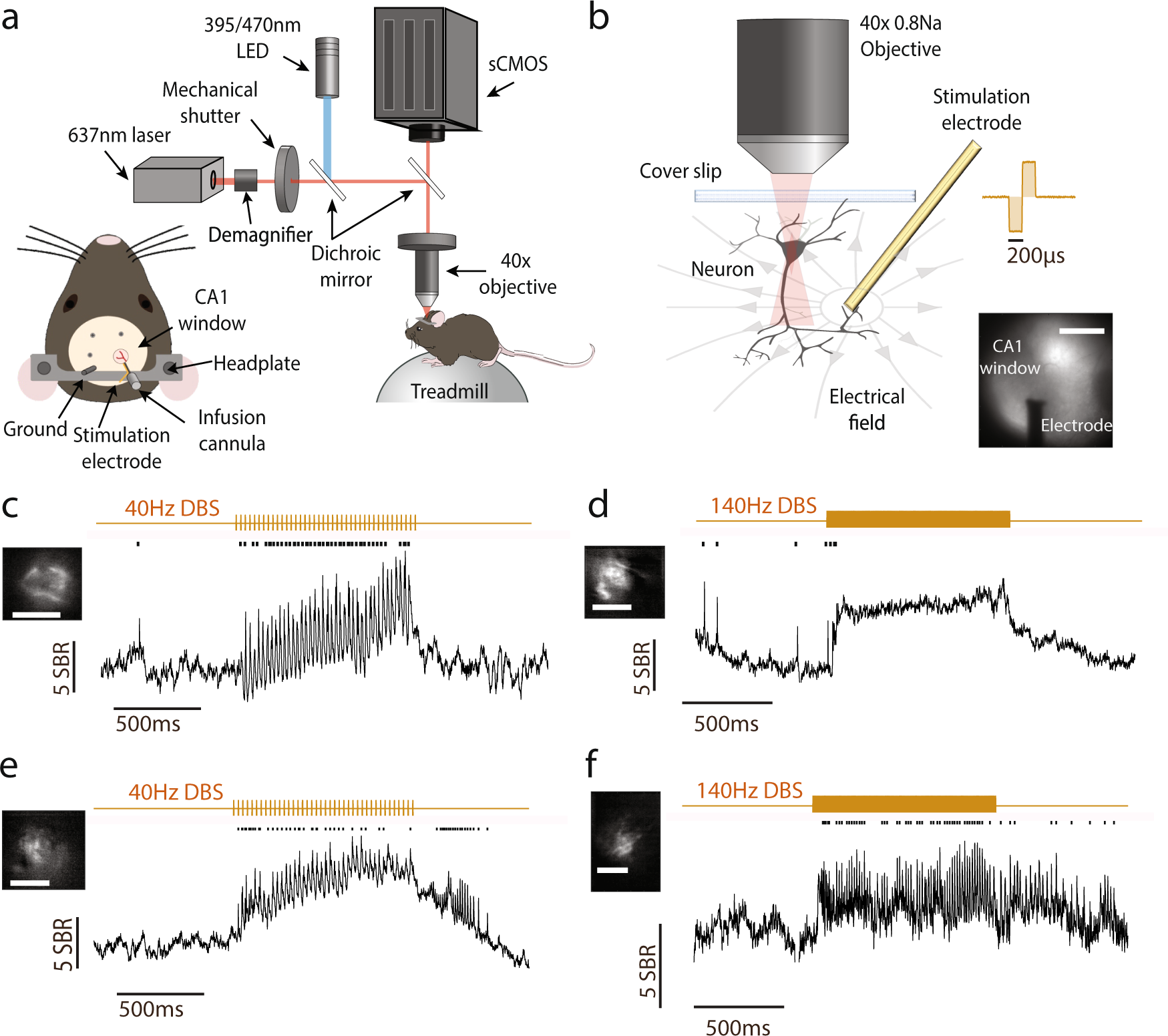
Deep brain stimulation creates informational lesion through

Long-distance in vivo neuromodulation with m-Torquer in freely
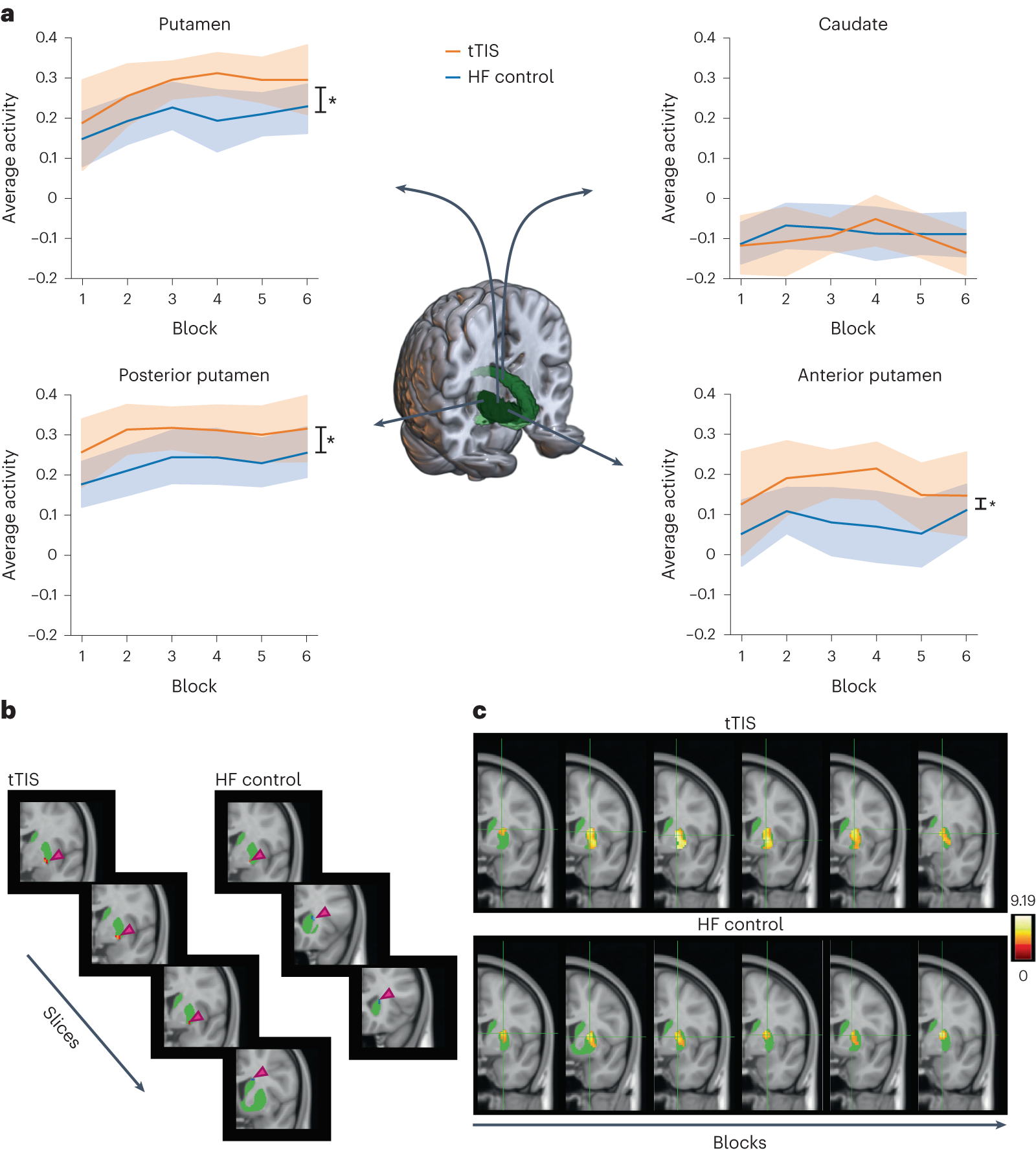
Noninvasive theta-burst stimulation of the human striatum enhances

Focal resting state frequency domain power analysis. (A) Power
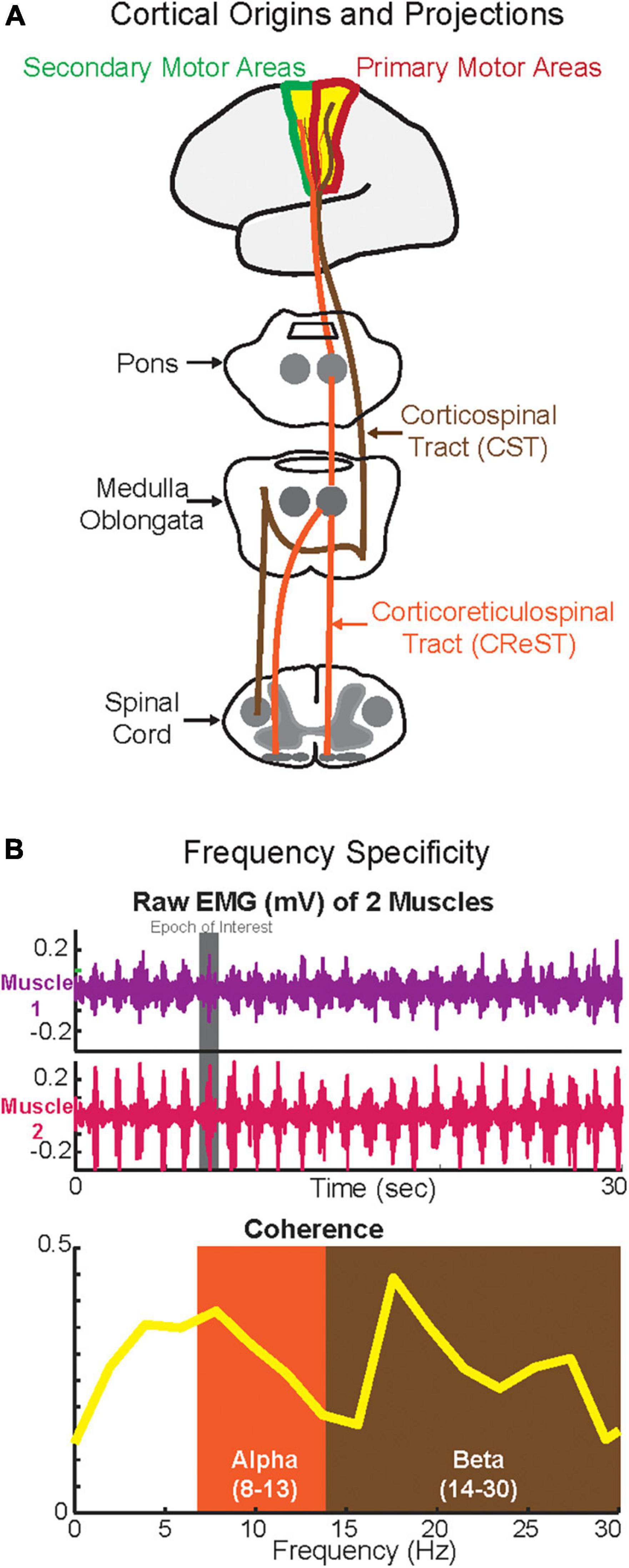
Frontiers Is there frequency-specificity in the motor control of
Recomendado para você
-
brain test 196|TikTok Search14 abril 2025
-
 Brain Test 4 Levels 156, 157, 158, 159, 160 Answers14 abril 2025
Brain Test 4 Levels 156, 157, 158, 159, 160 Answers14 abril 2025 -
 brain test nivel 41114 abril 2025
brain test nivel 41114 abril 2025 -
Water Sort Puzzle Color Sorting - Microsoft Apps14 abril 2025
-
 Easy Game - Brain Test Level 411-420 Walkthrough Solution (iOS14 abril 2025
Easy Game - Brain Test Level 411-420 Walkthrough Solution (iOS14 abril 2025 -
 Got the pink shorthair! : r/CatsAndSoup14 abril 2025
Got the pink shorthair! : r/CatsAndSoup14 abril 2025 -
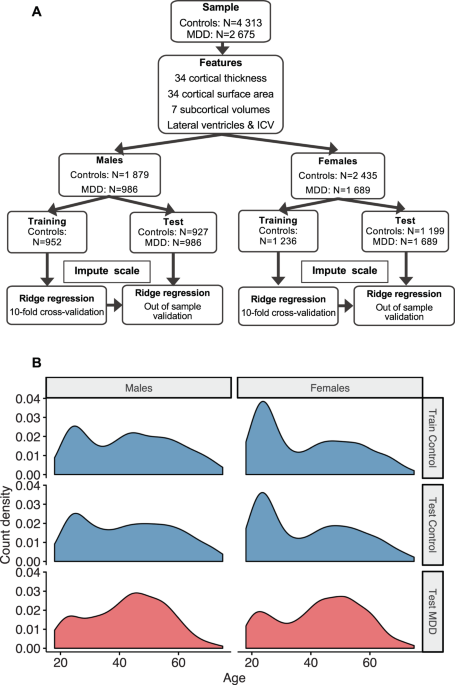 Brain aging in major depressive disorder: results from the ENIGMA14 abril 2025
Brain aging in major depressive disorder: results from the ENIGMA14 abril 2025 -
 Studies add details about the brain, clues for future treatments14 abril 2025
Studies add details about the brain, clues for future treatments14 abril 2025 -
 208 And 482 In 1 Game Card, Super Combo Game14 abril 2025
208 And 482 In 1 Game Card, Super Combo Game14 abril 2025 -
 anoosha syed14 abril 2025
anoosha syed14 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Steam Community :: Video :: Testing Some Mods in Mercenaries With Pvimto - Resident Evil 514 abril 2025
Steam Community :: Video :: Testing Some Mods in Mercenaries With Pvimto - Resident Evil 514 abril 2025 -
 Chess World Cup: R Praggnanandhaa-Magnus Carlsen Game 2 Drawn, Final Moves To Tie-Breakers14 abril 2025
Chess World Cup: R Praggnanandhaa-Magnus Carlsen Game 2 Drawn, Final Moves To Tie-Breakers14 abril 2025 -
 Poppy Playtime Chapter 2 Free Download PC Game pre installed with direct links and All dlcs included, Easy to install and play…14 abril 2025
Poppy Playtime Chapter 2 Free Download PC Game pre installed with direct links and All dlcs included, Easy to install and play…14 abril 2025 -
 Bola Basquete Spalding Highlight - Preto+Azul14 abril 2025
Bola Basquete Spalding Highlight - Preto+Azul14 abril 2025 -
 BBC Brasil14 abril 2025
BBC Brasil14 abril 2025 -
 Clientes na China compram produto de carne de burro 'contaminado14 abril 2025
Clientes na China compram produto de carne de burro 'contaminado14 abril 2025 -
 NARUTO SHIPPUDEN: Ultimate Ninja STORM 414 abril 2025
NARUTO SHIPPUDEN: Ultimate Ninja STORM 414 abril 2025 -
 Real Drift Car Racing Free APK for Android - Download14 abril 2025
Real Drift Car Racing Free APK for Android - Download14 abril 2025 -
 Fatal Fury Special - IGN14 abril 2025
Fatal Fury Special - IGN14 abril 2025 -
 Commission: Basil Plush Doll by Miss-Sarasa-Designs on DeviantArt14 abril 2025
Commission: Basil Plush Doll by Miss-Sarasa-Designs on DeviantArt14 abril 2025