Menin protein protects against aging and cognitive decline
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 17 abril 2025
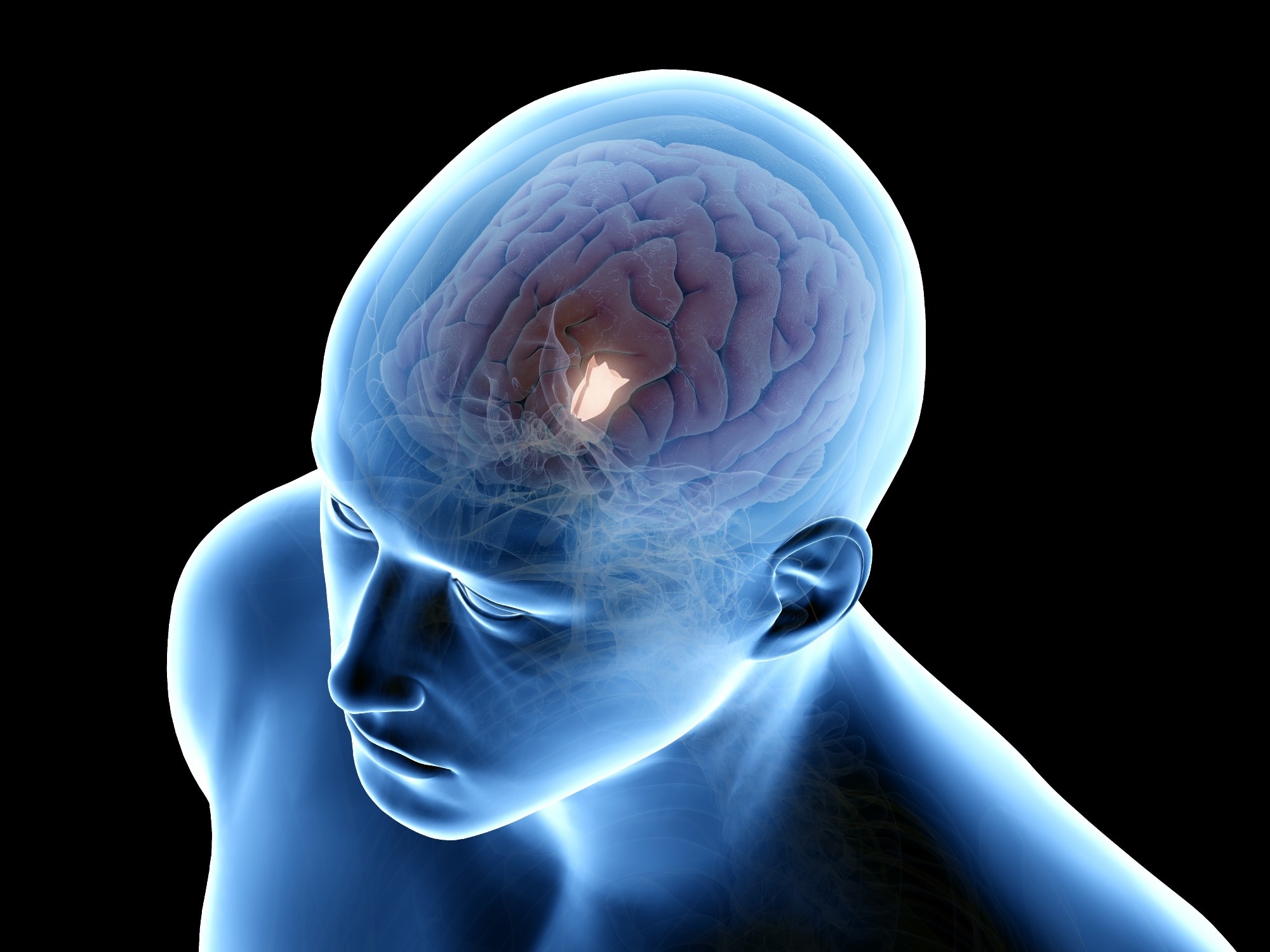
In a recent study published in the journal PLoS Biology, researchers from the University of Xiamen, China, explored the role of the hypothalamic menin in driving aging and associated cognitive decay.
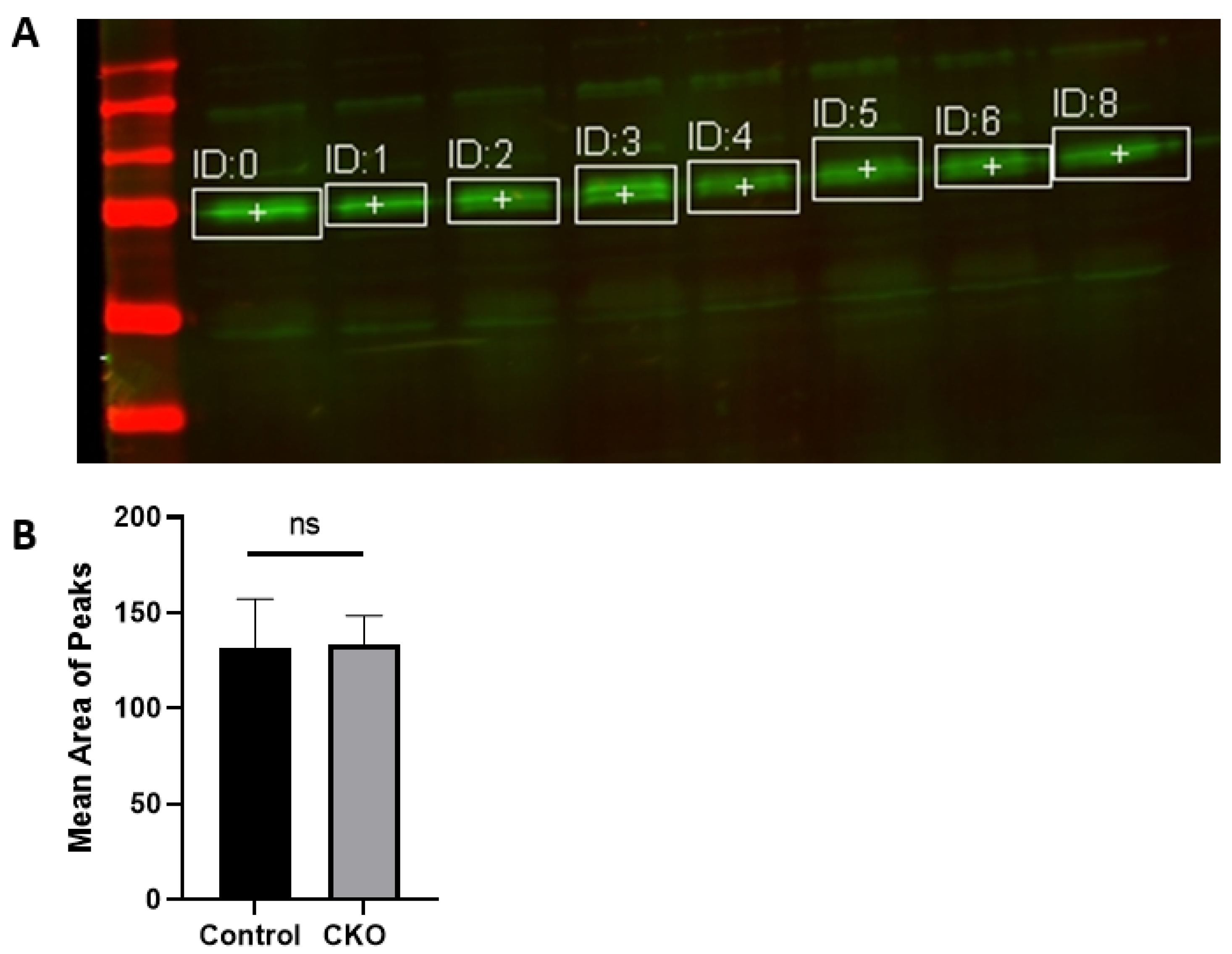
Cells, Free Full-Text

Previously Unknown Driver of Aging Discovered – Simple Supplement
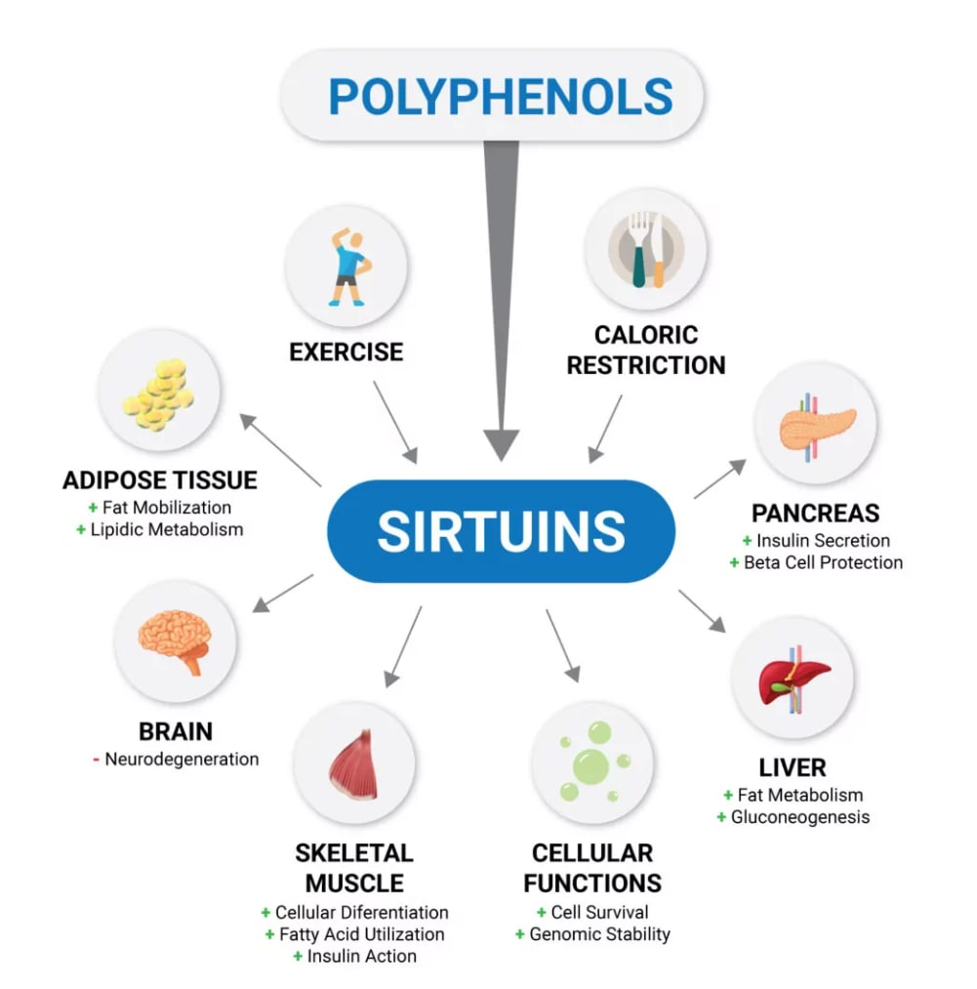
Current Anti-Aging Therapeutics

Cells, Free Full-Text

Menin Ser487 phosphorylation leads to enhanced binding to nuclear
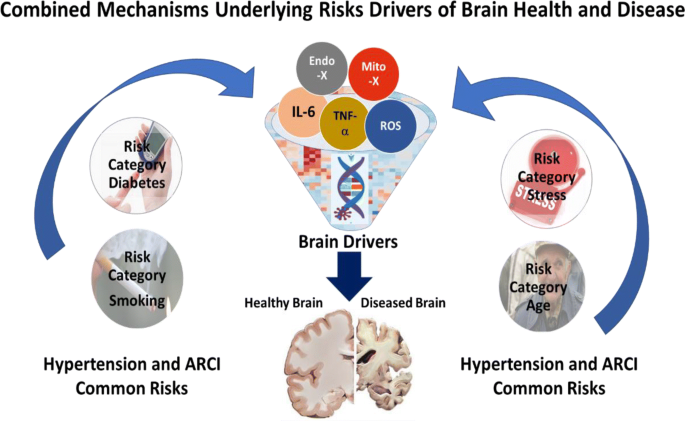
Hypertension and Age-Related Cognitive Impairment: Common Risk

Menin protein protects against aging and cognitive decline

Menin Ser487 phosphorylation leads to enhanced binding to nuclear

Scientists used menin to reverse aging in mice: Can they do it in

Scientists Suggest Simple Supplement To Combat Key Protein That
Hypothalamic Menin regulates systemic aging and cognitive decline
Does rapamycin slow down the accumulation of DNA damage in mice
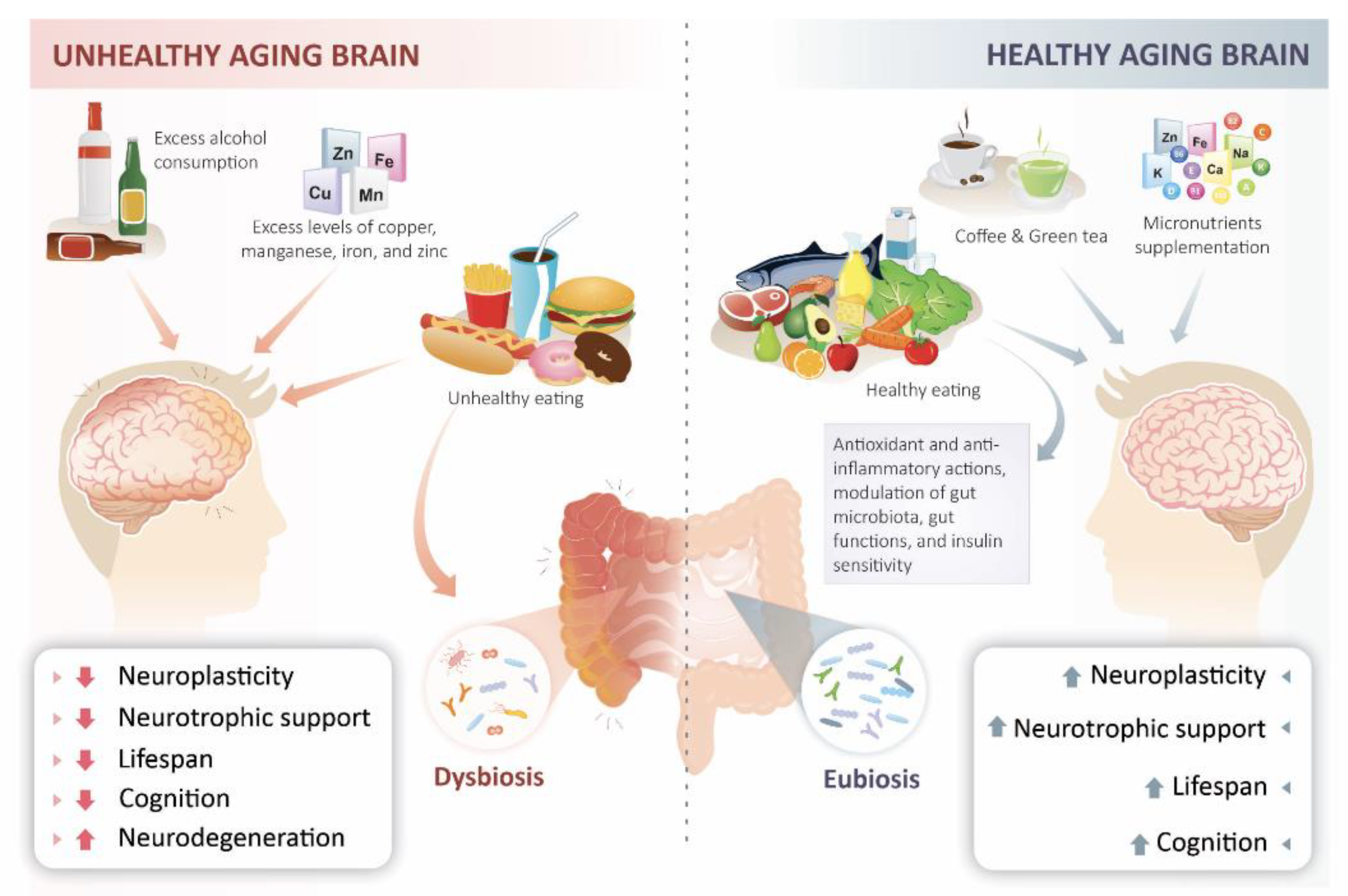
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Decline in the hypothalamic Menin may play a key role in aging
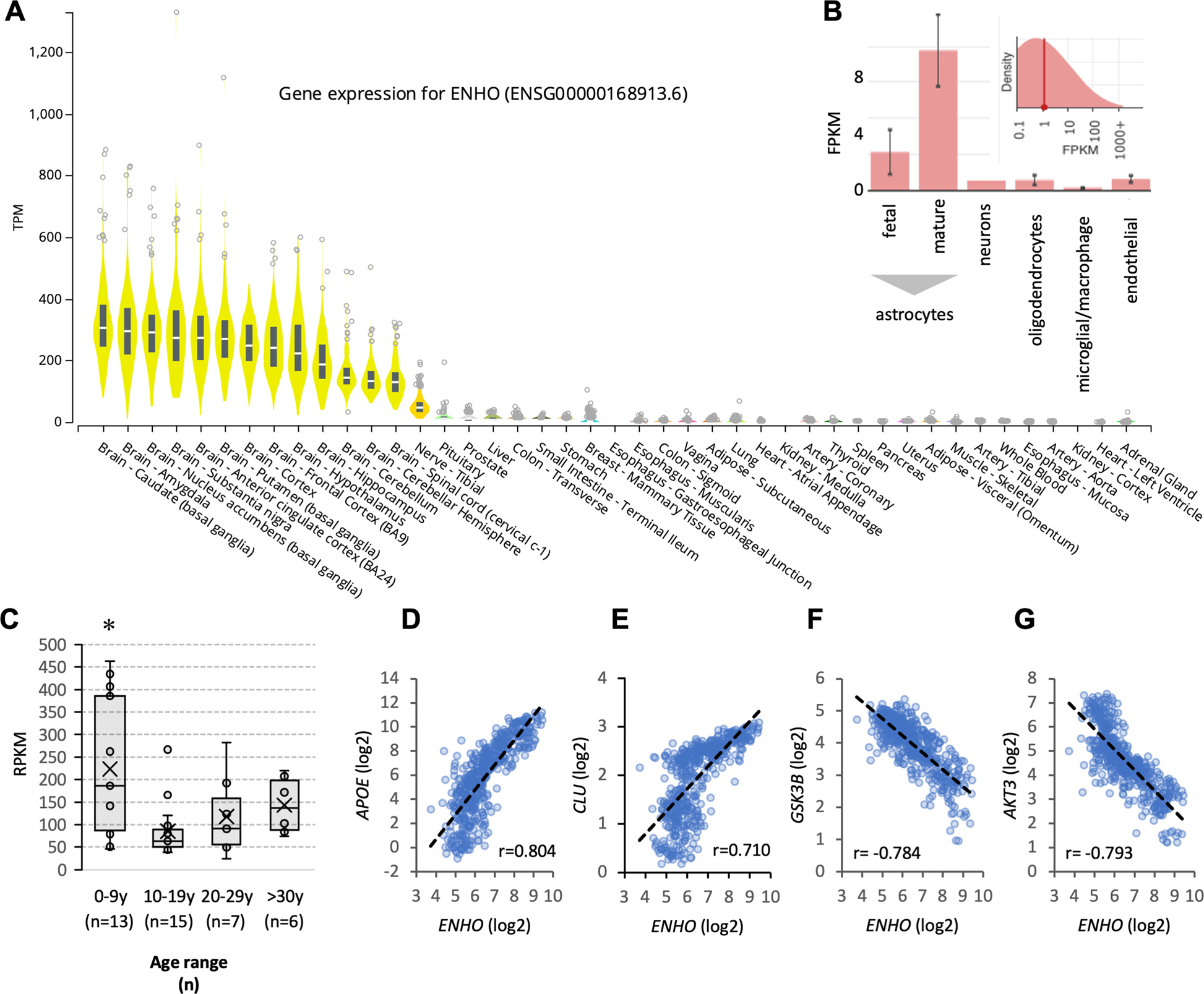
Adropin correlates with aging-related neuropathology in humans and
Recomendado para você
-
 Rosto de meninas bonitas17 abril 2025
Rosto de meninas bonitas17 abril 2025 -
 Julie Menin 202317 abril 2025
Julie Menin 202317 abril 2025 -
 Menin Seeks Re-Election to City Council in District 5 on UES17 abril 2025
Menin Seeks Re-Election to City Council in District 5 on UES17 abril 2025 -
 Investidor do Atlético-MG, Rubens Menin projeta crescimento do futebol brasileiro17 abril 2025
Investidor do Atlético-MG, Rubens Menin projeta crescimento do futebol brasileiro17 abril 2025 -
 Rafael Menin, da MRV, acredita em mudanças no programa habitacional do governo17 abril 2025
Rafael Menin, da MRV, acredita em mudanças no programa habitacional do governo17 abril 2025 -
 Atlético-MG: Menin se manifesta pela primeira vez após transição para SAF17 abril 2025
Atlético-MG: Menin se manifesta pela primeira vez após transição para SAF17 abril 2025 -
 Molecules, Free Full-Text17 abril 2025
Molecules, Free Full-Text17 abril 2025 -
 ISABELLE MENIN - Artists - Muriel Guepin Gallery17 abril 2025
ISABELLE MENIN - Artists - Muriel Guepin Gallery17 abril 2025 -
 Tudo sobre Rubens Menin · Notícias da TV17 abril 2025
Tudo sobre Rubens Menin · Notícias da TV17 abril 2025 -
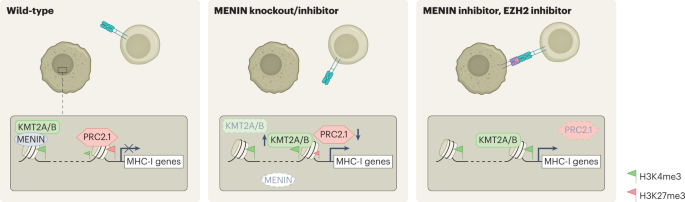 Dissecting MENIN in bivalent gene regulation17 abril 2025
Dissecting MENIN in bivalent gene regulation17 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
Atividade 06, PDF, Aquífero17 abril 2025
-
 DISMISS definição e significado17 abril 2025
DISMISS definição e significado17 abril 2025 -
 Link's Awakening Walkthrough - The Awakening - Game Boy Color - Zelda Dungeon17 abril 2025
Link's Awakening Walkthrough - The Awakening - Game Boy Color - Zelda Dungeon17 abril 2025 -
 Did You Know - There Are Still 3 Coded Messages From WWII That Haven't Been Decrypted Yet, but we are still working on them!17 abril 2025
Did You Know - There Are Still 3 Coded Messages From WWII That Haven't Been Decrypted Yet, but we are still working on them!17 abril 2025 -
 Epic Face png images17 abril 2025
Epic Face png images17 abril 2025 -
 Xbox 360 jogo futebol pes 2022, extra17 abril 2025
Xbox 360 jogo futebol pes 2022, extra17 abril 2025 -
![UPDATED) NEW TIER LIST, Your Bizarre Adventure [YBA Update 1.55]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KDg0Rhm_Y8M/maxresdefault.jpg) UPDATED) NEW TIER LIST, Your Bizarre Adventure [YBA Update 1.55]17 abril 2025
UPDATED) NEW TIER LIST, Your Bizarre Adventure [YBA Update 1.55]17 abril 2025 -
 Livro - Banana Fish Vol. 517 abril 2025
Livro - Banana Fish Vol. 517 abril 2025 -
 File:Classic sonic nose.svg - Sonic Retro17 abril 2025
File:Classic sonic nose.svg - Sonic Retro17 abril 2025 -
 Kawaii Fofa, Garotas17 abril 2025
Kawaii Fofa, Garotas17 abril 2025
