Polymers, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 16 abril 2025
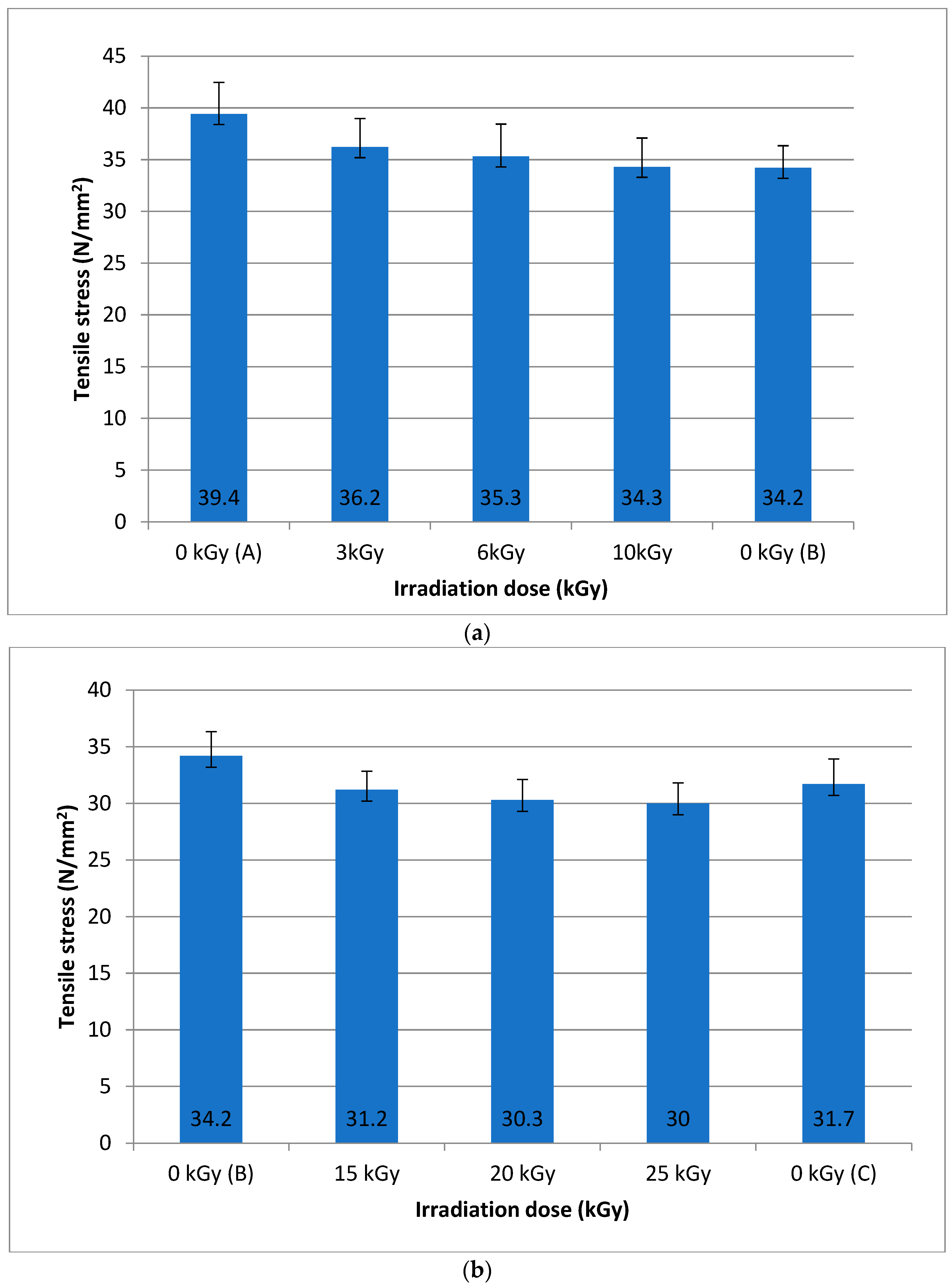
The historical artefacts of parchment are prone to degradation if the storage conditions are improper due to the collagen structure having a limited stability under physical, chemical, and biological agent attacks. The parchment structure is difficult to characterize due to the variety of manufacturing traditions (eastern/western), intrinsic variability of skins (i.e., species, breeding variation, living conditions, effects of pathologies, etc.), biodeterioration, and aging, and the main concern in its analysis is its uniformity. The deterioration of parchment collagen produces a rather stiff or in some circumstances, a relaxed structure. Any intervention or treatment of unique, very precious cultural heritage artefacts must not negatively influence the properties of the component materials. Gamma irradiation is a relatively new technique of bioremediation. Data on the leather properties pre- and post-ionizing radiation bioremediation treatments are few in the literature. Fewer data are available on the historical leather and parchment physical chemical characteristics after ionizing gamma irradiation. This research had two main objectives: (i) the characterization of the parchment structure’s uniformity across the analyzed areas and its mechanical properties, i.e., tensile stress by mechanical tests and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy; and (ii) to establish parchment tolerance when exposed to ionizing gamma radiation as a pre-requisite for cultural heritage preservation irradiation treatment. It was found that the mechanical tests and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy may identify changes in the parchment’s irradiated structure and that the preservation of cultural heritage parchment artefacts may be performed at maximum 15 kGy gamma irradiation dose.
Introductory polymer chemistry : Misra, G. S. (Gauri Shankar) : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
10.2: Polymers and Plastics - Engineering LibreTexts

Methods for Studying Three-Dimensional Free-Radical Polymerization and Cross-Linked Polymers

Journal of Applied Polymer Science

Chemical recycling systems for closed-loop circular polymers. (a)

Biosynthetic Polymers as Functional Materials

Solvent‐Free Chemical Recycling of Polymethacrylates made by ATRP and RAFT polymerization: High‐Yielding Depolymerization at Low Temperatures - Whitfield - 2023 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley Online Library

Sustainable polymers from biomass: Bridging chemistry with materials and processing - ScienceDirect

Polymers from Renewable Resources: Sage Journals
PDF) Strategies to Improve Photodynamic Therapy Efficacy of Metal-Free Semiconducting Conjugated Polymers

Biosynthetic Polymers as Functional Materials

Polymer, Description, Examples, Types, Material, Uses, & Facts
Polymer Blends: Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part C: Vol 18, No 1

Polymerization, Definition, Classes, & Examples
Recomendado para você
-
 Supreme Values - Your Source for MM2 Values!16 abril 2025
Supreme Values - Your Source for MM2 Values!16 abril 2025 -
 Compressive Strength Values (in N/mm 2 )16 abril 2025
Compressive Strength Values (in N/mm 2 )16 abril 2025 -
Solved b) Calculate the value of stress in N/mm2 and16 abril 2025
-
Oiles SPB-405030 Box of 4 Straight Bushing - 40 mm ID - IMS Supply16 abril 2025
-
 The state of stress on a element in plane stress is shown as in the figure.What is the value of σ if the values of the principal stresses are 164 N/mm2 and16 abril 2025
The state of stress on a element in plane stress is shown as in the figure.What is the value of σ if the values of the principal stresses are 164 N/mm2 and16 abril 2025 -
 Stability of different fixation methods after reduction malarplasty under average and maximum masticatory forces: a finite element analysis, BioMedical Engineering OnLine16 abril 2025
Stability of different fixation methods after reduction malarplasty under average and maximum masticatory forces: a finite element analysis, BioMedical Engineering OnLine16 abril 2025 -
Solved Note: The value of E for steel is 205000 N/mm2. The16 abril 2025
-
 Autopipe Code Stress for DNVGL-ST-F101:2017 - AutoPIPE Forum - AutoPIPE - Bentley Communities16 abril 2025
Autopipe Code Stress for DNVGL-ST-F101:2017 - AutoPIPE Forum - AutoPIPE - Bentley Communities16 abril 2025 -
 Ste db etg88-100_rgb_en16 abril 2025
Ste db etg88-100_rgb_en16 abril 2025 -
 WinGraf error - SOFiSTiK - SOFiSTiK Forum16 abril 2025
WinGraf error - SOFiSTiK - SOFiSTiK Forum16 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Jogue Ludo 2 Jogadores online de graça em16 abril 2025
Jogue Ludo 2 Jogadores online de graça em16 abril 2025 -
Portal Piece - E agora que Zoro está com a espada do Oden, será se daria uma luta boa com Mihawk?! - pandaman16 abril 2025
-
 O chef particular de Chris Hemsworth revela detalhes da dieta extrema do ator contra o Alzheimer - GDSNews16 abril 2025
O chef particular de Chris Hemsworth revela detalhes da dieta extrema do ator contra o Alzheimer - GDSNews16 abril 2025 -
 away-win-or-draw-football-predictions - Confirmbets - Football16 abril 2025
away-win-or-draw-football-predictions - Confirmbets - Football16 abril 2025 -
flowey battle|TikTok Search16 abril 2025
-
 Convite Animado Gatinha Marie RA Produção Visual16 abril 2025
Convite Animado Gatinha Marie RA Produção Visual16 abril 2025 -
 Music Video for The Quintessential Quintuplets Movie Theme Song Released16 abril 2025
Music Video for The Quintessential Quintuplets Movie Theme Song Released16 abril 2025 -
 Learn the songs to aid your quest to save Hyrule on your own Ocarina of Time16 abril 2025
Learn the songs to aid your quest to save Hyrule on your own Ocarina of Time16 abril 2025 -
 Youkoso Jitsuryoku Shijou Shugi no Kyoushitsu e 2nd Season Episode 716 abril 2025
Youkoso Jitsuryoku Shijou Shugi no Kyoushitsu e 2nd Season Episode 716 abril 2025 -
 Melhores Pokémon de Água em Brilliant Diamond & Shining Pearl16 abril 2025
Melhores Pokémon de Água em Brilliant Diamond & Shining Pearl16 abril 2025



