Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 14 abril 2025
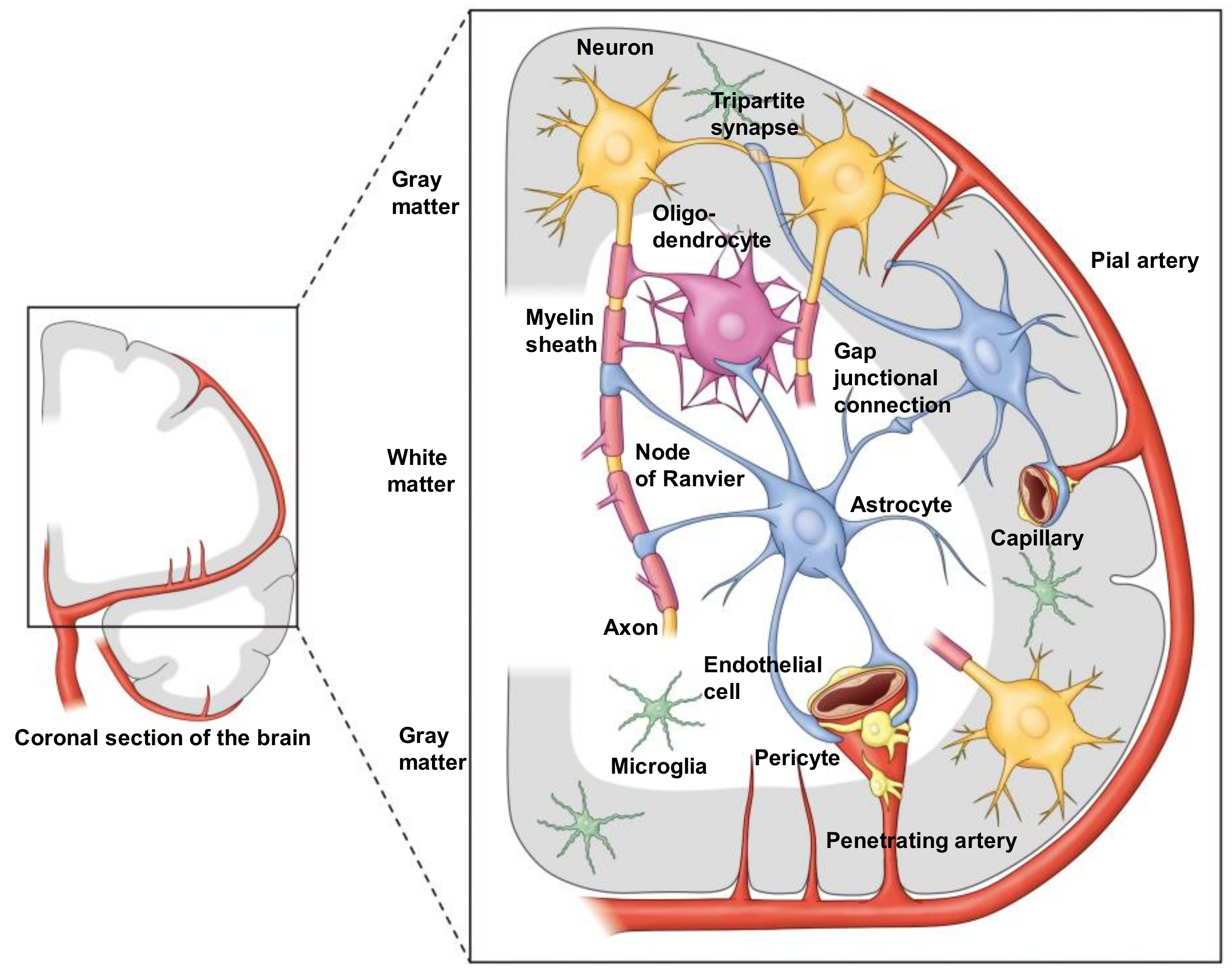
The neurovascular unit (NVU) is a conceptual framework that has been proposed to better explain the relationships between the neural cells and blood vessels in the human brain, focused mainly on the brain gray matter. The major components of the NVU are the neurons, astrocytes (astroglia), microvessels, pericytes, and microglia. In addition, we believe that oligodendrocytes should also be included as an indispensable component of the NVU in the white matter. Of all these components, astrocytes in particular have attracted the interest of researchers because of their unique anatomical location; these cells are interposed between the neurons and the microvessels of the brain. Their location suggests that astrocytes might regulate the cerebral blood flow (CBF) in response to neuronal activity, so as to ensure an adequate supply of glucose and oxygen to meet the metabolic demands of the neurons. In fact, the adult human brain, which accounts for only 2% of the entire body weight, consumes approximately 20–25% of the total amount of glucose and oxygen consumed by the whole body. The brain needs a continuous supply of these essential energy sources through the CBF, because there are practically no stores of glucose or oxygen in the brain; both acute and chronic cessation of CBF can adversely affect brain functions. In addition, another important putative function of the NVU is the elimination of heat and waste materials produced by neuronal activity. Recent evidence suggests that astrocytes play pivotal roles not only in supplying glucose, but also fatty acids and amino acids to neurons. Loss of astrocytic support can be expected to lead to malfunction of the NVU as a whole, which underlies numerous neurological disorders. In this review, we shall focus on historical and recent findings with regard to the metabolic contributions of astrocytes in the NVU.

Nucleic acid biomarkers of immune response and cell and tissue damage in children with COVID-19 and MIS-C - ScienceDirect
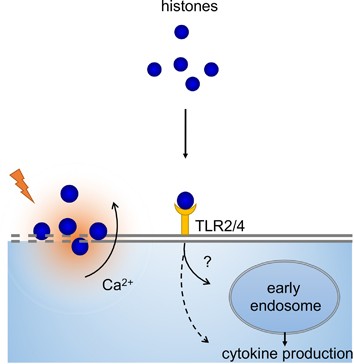
Extracellular histones, cell-free DNA, or nucleosomes: differences in immunostimulation
Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus B-30892 can inhibit cytotoxic effects and adhesion of pathogenic Clostridium difficile to Caco-2 cells, Gut Pathogens

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy

Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods, Microbial Cell Factories
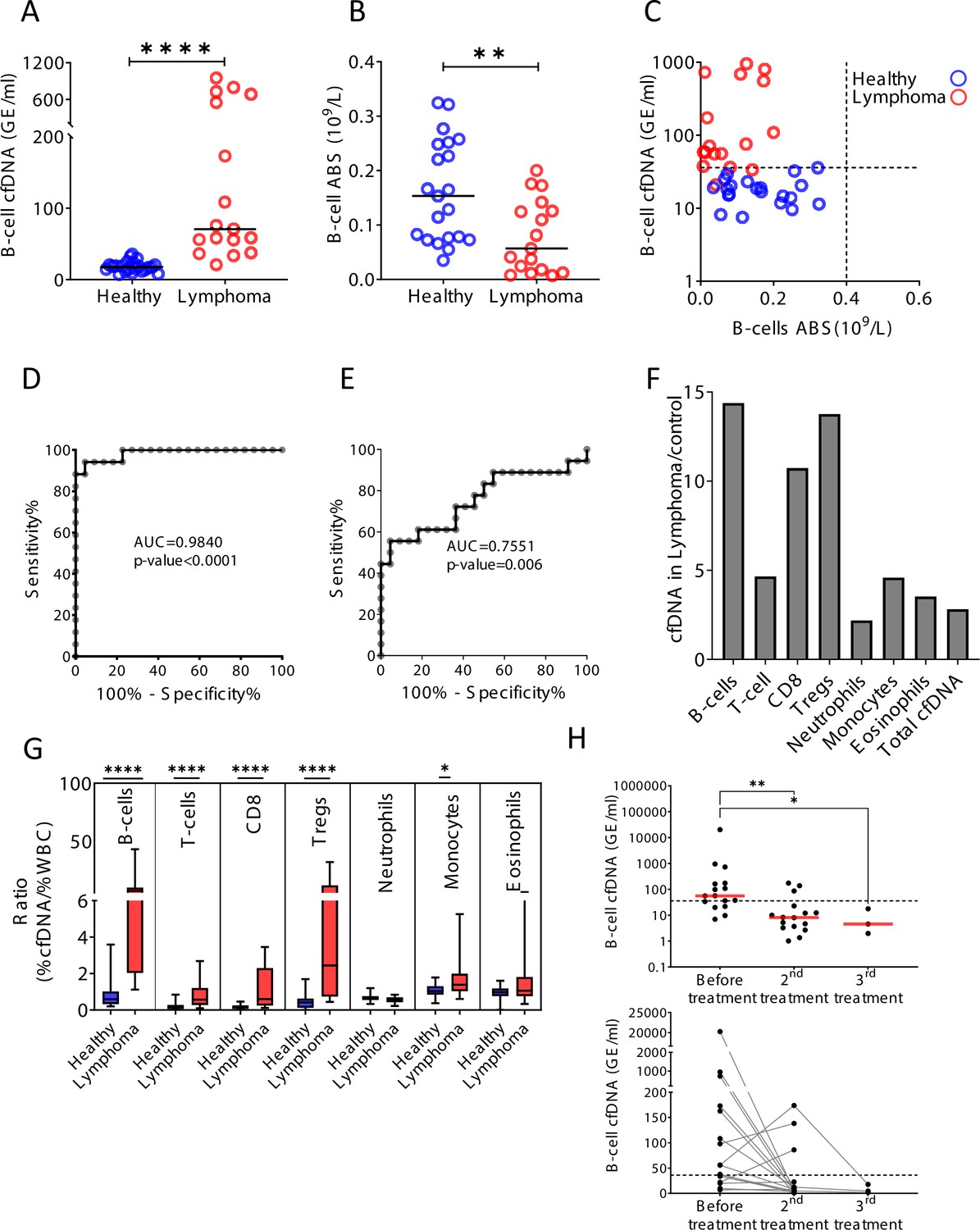
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA

Advances and applications of cell-free systems for metabolic production - ScienceDirect
THE LIVES OF A CELL : LEWIS THOMAS : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
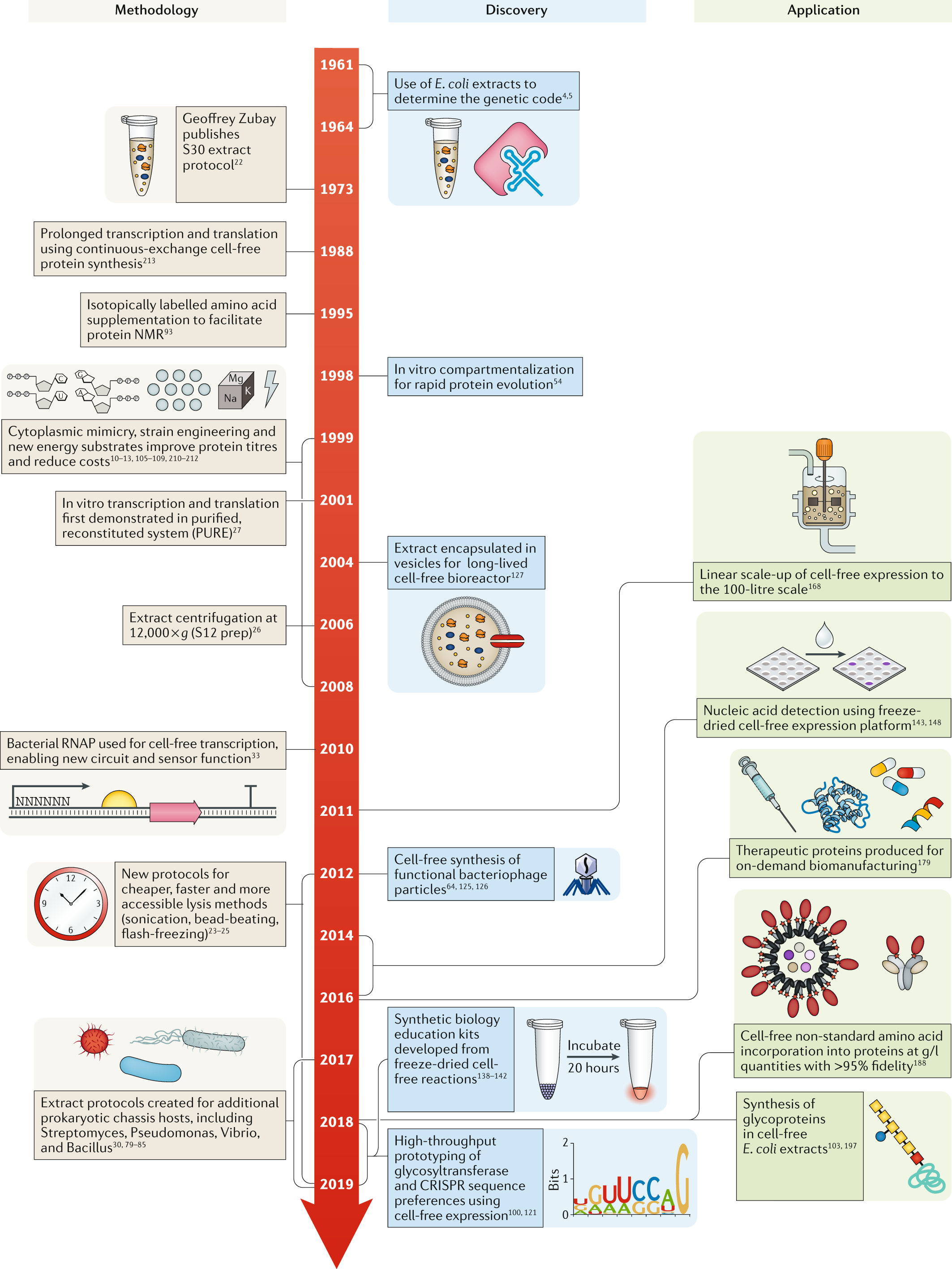
Cell-free gene expression: an expanded repertoire of applications

PDF) Comparative separation methods and biological characteristics of human placental and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in serum-free culture conditions

Streptomyces cell-free systems for natural product discovery and engineering - ScienceDirect
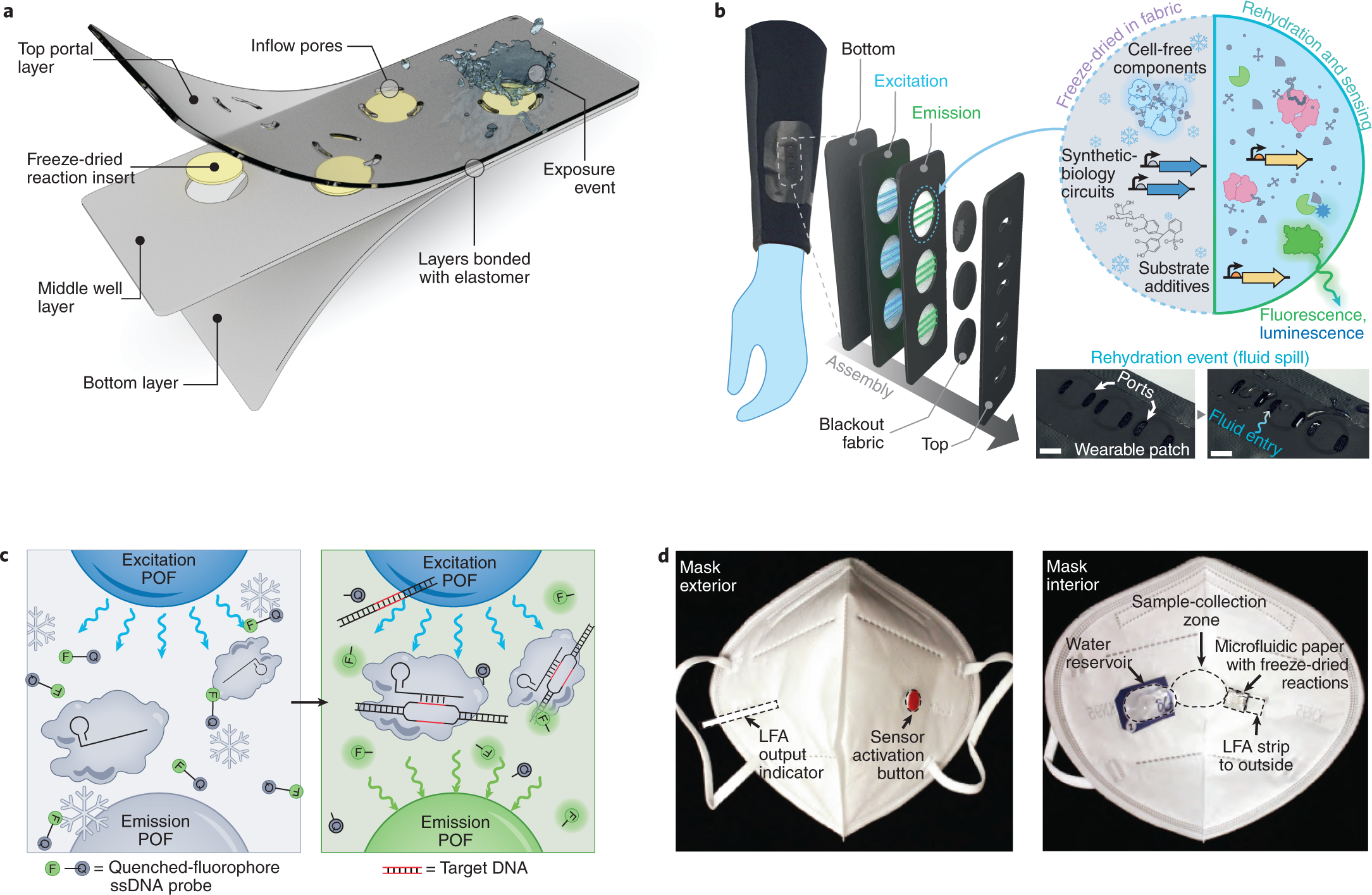
Textile-embedded cell-free biosensors
PDF) Protein structural biology using cell-free platform from wheat germ
IAPP/amylin-induced interaction between NLRP3 and ASC in a cell-free
Recomendado para você
-
 Você precisa conhecer Jesus14 abril 2025
Você precisa conhecer Jesus14 abril 2025 -
Keity Godoy14 abril 2025
-
 Kelly (Novembro/2002) Entrevistas do Painel do Basquete Feminino14 abril 2025
Kelly (Novembro/2002) Entrevistas do Painel do Basquete Feminino14 abril 2025 -
 Augite: Mineral information, data and localities.14 abril 2025
Augite: Mineral information, data and localities.14 abril 2025 -
 ANO XLV - VITÓRIA-ES, SEXTA-FEIRA, 11 DE NOVEMBRO DE 201114 abril 2025
ANO XLV - VITÓRIA-ES, SEXTA-FEIRA, 11 DE NOVEMBRO DE 201114 abril 2025 -
 Molecules, Free Full-Text14 abril 2025
Molecules, Free Full-Text14 abril 2025 -
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/68662479/716804.5.jpg) Across State Lines: Henderson Reportedly Leaving Seattle - The14 abril 2025
Across State Lines: Henderson Reportedly Leaving Seattle - The14 abril 2025 -
 Live Updates & Results European Championships Black Belt Day 114 abril 2025
Live Updates & Results European Championships Black Belt Day 114 abril 2025 -
 PESQUISAS E DEBATES SOBRE A SAÚDE COLETIVA: UM INTERCÂMBIO ENTRE14 abril 2025
PESQUISAS E DEBATES SOBRE A SAÚDE COLETIVA: UM INTERCÂMBIO ENTRE14 abril 2025 -
 Education Archives - The Dialogue14 abril 2025
Education Archives - The Dialogue14 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Tsume Inuzuka Anime naruto, Naruto art, Naruto fan art14 abril 2025
Tsume Inuzuka Anime naruto, Naruto art, Naruto fan art14 abril 2025 -
 One-Punch Man, Vol. 24: Volume 2414 abril 2025
One-Punch Man, Vol. 24: Volume 2414 abril 2025 -
 Tv-friends-1 GIFs - Get the best GIF on GIPHY14 abril 2025
Tv-friends-1 GIFs - Get the best GIF on GIPHY14 abril 2025 -
 Level 32 - The Skeleton Forest, The Backrooms Experience: Alternative Dimension Wiki14 abril 2025
Level 32 - The Skeleton Forest, The Backrooms Experience: Alternative Dimension Wiki14 abril 2025 -
 All Star Cano Alto ou Médio Tênis Feminino e Masculino14 abril 2025
All Star Cano Alto ou Médio Tênis Feminino e Masculino14 abril 2025 -
 Always on My Mind (Clarinet and Piano)14 abril 2025
Always on My Mind (Clarinet and Piano)14 abril 2025 -
 Piano Digital Casio CDPS160 Vermelho Kit Completo - Super Sonora!14 abril 2025
Piano Digital Casio CDPS160 Vermelho Kit Completo - Super Sonora!14 abril 2025 -
 Will There Be a New Harry Potter Movie in 2023?14 abril 2025
Will There Be a New Harry Potter Movie in 2023?14 abril 2025 -
 Jumpscares (UCN), Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki14 abril 2025
Jumpscares (UCN), Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki14 abril 2025 -
 Palkia VSTAR Astral radiance Deck - PokemonCard14 abril 2025
Palkia VSTAR Astral radiance Deck - PokemonCard14 abril 2025
